Top Ten Types of Plagiarism Infographic
Plagiarism is said to occur when someone takes the work or ideas from another person and uses or presents them as his or her own ideas. According to (Meriam Webster, 2016), plagiarism is stealing and passing off (the ideas or words of another) as one’s own or using the production of another without giving credit to the source. In order to detect plagiarism, an online plagiarism checker can be used to point out plagiarised content.
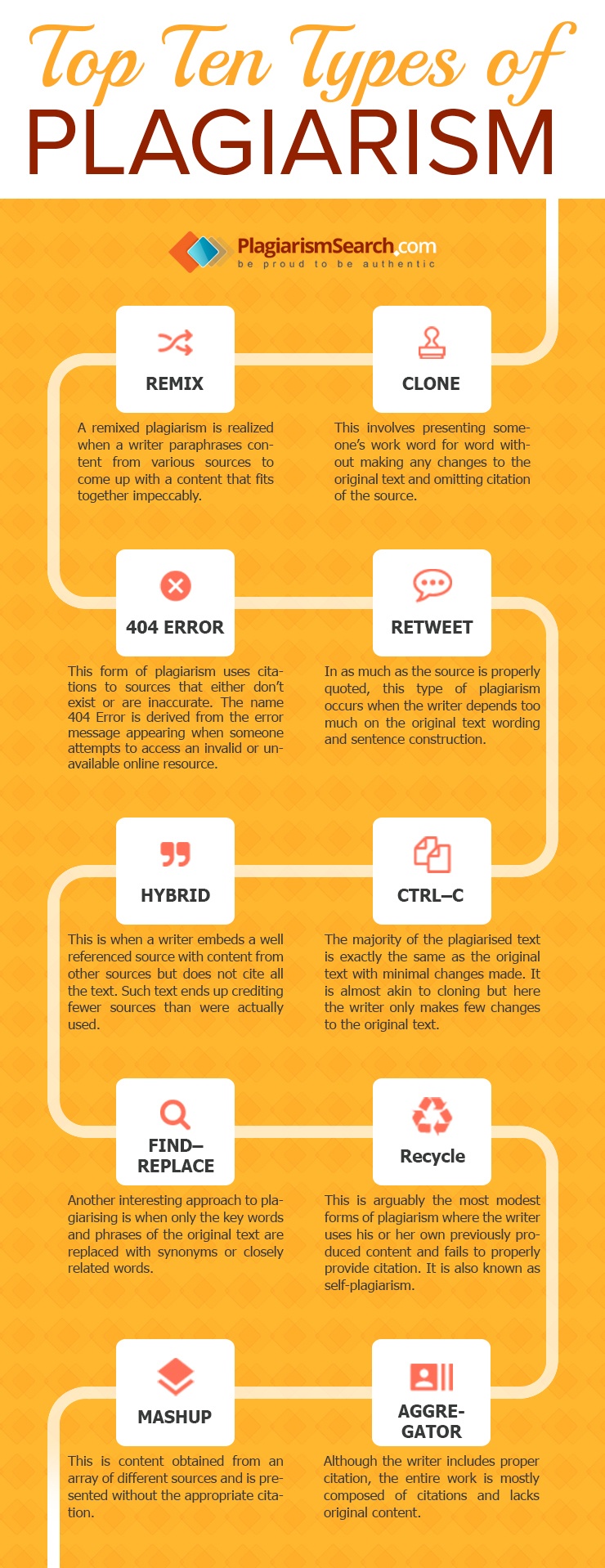
Types of plagiarism
There are several types of plagiarism depending on how the person framed or modified the original content. In this infographic ten common types of plagiarism (as outlined by White Paper, 2012) are examined. A plagiarism detector can be used to identify most but not necessarily all of the below types of plagiarism.
- Clone: This involves presenting someone’s work word for word without making any changes to the original text and omitting citation of the source.
- Remix: A remixed plagiarism is realized when a writer paraphrases content from various sources to come up with a content that fits together impeccably.
- 404 Error: This form of plagiarism uses citations to sources that either don’t exist or are inaccurate. The name 404 Error is derived from the error message appearing when someone attempts to access an invalid or unavailable online resource.
- Retweet: In as much as the source is properly quoted, this type of plagiarism occurs when the writer depends too much on the original text wording and sentence construction.
- Hybrid: This is when a writer embeds a well referenced source with content from other sources but does not cite all the text. Such text ends up crediting fewer sources than were actually used.
- CTRL – C: The majority of the plagiarised text is exactly the same as the original text with minimal changes made. It is almost akin to cloning but here the writer only makes few changes to the original text.
- Find – Replace: Another interesting approach to plagiarising is when only the key words and phrases of the original text are replaced with synonyms or closely related words.
- Recycle: This is arguably the most modest forms of plagiarism where the writer uses his or her own previously produced content and fails to properly provide citation. It is also known as self-plagiarism.
- Mashup: This is content obtained from an array of different sources and is presented without the appropriate citation.
- Aggregator: Although the writer includes proper citation, the entire work is mostly composed of citations and lacks original content.
See also: Paraphrase Vs Plagiarism Infographic





You can adjust your cookie preferences here.