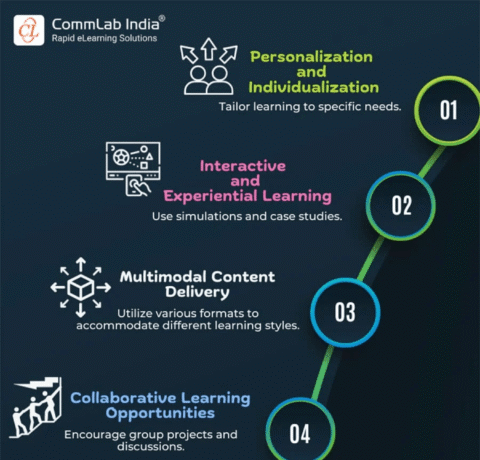
Instructional Design Models Infographic
An instructional design model is used to define the activities that will guide the development of eLearning projects. It allows you to communicate the purpose and reason behind a strategy. A framework gives you the birds-eye view of all the major components that have to be included in the course. The Instructional Design Models Infographic presents the most widely used models that eLearning designers acknowledge and use to structure and plan their training.
ADDIE Model
ADDIE stands for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. Each phase of the model offers an opportunity for iterations and changes before moving to the next one. Here is a brief description of each step of the ADDIE process:
- Analysis — Why is the training needed? The instructional designers (IDs) answer this question after exhaustively collecting information and profiling target learners, and understanding the needs and expectations of the organization. Analysis drives design and the development process.
- Design —In this phase, IDs select the instructional strategy to follow, write objectives, choose appropriate media and delivery methods.
- Development — IDs utilize agreed expectations from the Design phase to develop the course materials.
- Implementation — The course is released/rolled-out, delivered, to the learners, and its impact is monitored.
- Evaluation — Is the course providing the expected results? IDs collaborate with the client and evaluate the impact of the course based on learner feedback, surveys, and even analytics.
Once the evaluation is complete, the results are converted into actionable improvements. The whole ADDIE process is repeated.
Merrill’s Principles of Instruction
Proposed by David Merril in 2002, this framework holistically integrates five principles of learning, namely:
- Task-centered principle
- Activation principle
- Demonstration principle
- Application principle
- Integration principle
The principles promote learning in the following manner:
- Learning starts with real-world problems. Students should be able to relate to problems and tasks they can handle.
- A course must activate existing knowledge base of the learner; hence aiding them connect previous knowledge with the new one.
- A course must demonstrate the knowledge (both visually and through story telling) so that it leverages different regions of the brain, hence retaining it longer.
- Allow them to apply new information on their own. Let them practice and learn from their mistakes. Let them see how your new material works in concrete situations
- The course must offer possibilities for integrating the knowledge into the learner’s world through discussion, reflection, and/or presentation of new knowledge.
Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction
Robert Gagne proposed a framework comprising of a series of events based on the behaviourist approach to learning. These events follow a systematic instructional design process, creating a flexible model where events can be adapted to cater to different learning situations. It is, in fact, one of the most used instructional design models as it provides a sound structure for developing effective eLearning.
The nine events of instruction are:
- Gain attention of the students —with stimuli that catch and engage their brain (novel ideas or thought-provoking question, etc.)
- Inform students of the objectives — Establish the expected outcomes and criteria for measuring achievement.
- Stimulate recall of prior learning —Leverage existing knowledge before introducing new knowledge and build on it.
- Present the content — Deliver the content in easily consumable chunks.
- Provide learner guidance — Guide them with examples, case studies, and other instructional support to supplement the content.
- Elicit performance — Engage them with different activities that recall, utilize, and evaluate knowledge.
- Provide feedback — Reinforce knowledge with immediate feedback (informative, remedial, corrective, etc.)
- Assess performance —Test their knowledge with established (and transparent) criteria.
- Enhance retention and transfer to the job — Use content retention strategies (concept maps, rephrasing, summarizing, job aids, etc.)
Bloom’s Taxonomy
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom created a classification system of measurable verbs to describe and organize the different levels of cognitive learning. In 2001, the six dimensions were modified by Anderson and Krathwohl and are known as the "Revised Taxonomy."
The taxonomy pushes the learners past the lower steps of learning (of knowledge and remembering) and into the domain of deeper understanding, reflection, and application of knowledge to develop a learner’s individual process of solving problems. It is a great way for establishing learning objectives that engage learners with the content and ingraining new knowledge and concepts.





You can adjust your cookie preferences here.