Design Theories and Principles That eLearning Designers Should Know
- C.R.A.P. for Effective Visual Design
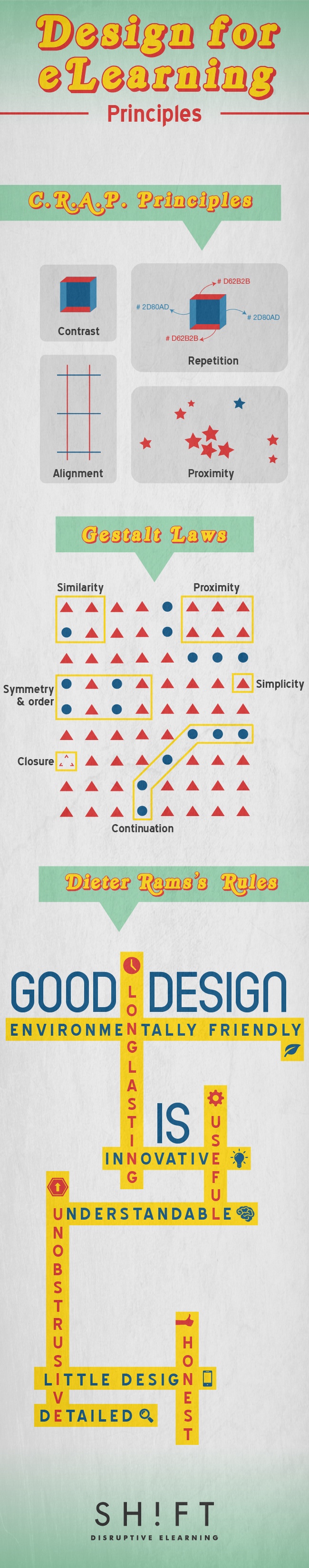
The 4 basic principles present in every eLearning design can be abbreviated to CRAP.- Contrast
Any two items that are not exactly the same should be very different. - Repetition
eLearning designers should repeat certain design elements throughout the course. - Alignment
Different aspects of the design should line up in columns, rows, and along a centerline. - Proximity
Developers should group related items together.
- Contrast
- Gestalt for Coherence
There are 6 principles of Gestalt, which work together to ensure learners form a positive opinion about the design from the first glance. These principles are:- Similarity
Elements that are similar to one another merge into groups almost automatically. - Proximity
The idea that when learners sees several objects arranged together, they perceive these objects as belonging to a group. - Closure
The mind fills incomplete space with the missing information. - Simplicity
The mind will attempt to turn visual chaos into something more simple and understandable. - Continuation
The human eye naturally wants to move from one object to another. - Symmetry and order
The mind tries to perceive objects as symmetrical and based around a central point. This is because it makes sense to perceptually divide objects evenly and turn random, unconnected items into something understandable.
Read this article: Understanding and Using the Laws of Perception in eLearning Design
- Similarity
- Dieter Rams’s Principles of Good Design
In the early 1980s, Dieter Rams set out the following 10 principles:- Good Design Is Innovative
Innovative design has the element of surprise, which stops students from becoming bored and improves learners’ ability to encode new information. - Good Design Makes a Product Useful
Learners must find content useful to find value in it. Without perceived usefulness, students will learn very little. - Good Design Is Aesthetic
Aesthetics go hand in hand with usefulness. A course must be appealing in order for users to want to spend time with the content. - Good Design Makes a Product Understandable
The “product” in this sense is the eLearning course. It should consist of content relevant to learners’ needs by taking into account the skills students currently possess while providing learners with material that will lead them to obtaining the knowledge they desire. - Good Design Is Unobtrusive
Courses are tools to fulfill a purpose; therefore, eLearning design must be unobtrusive to leave room for self-expression. - Good Design Is Honest
Modules and objectives must all promise only what they can actually offer learners. When eLearning design ensures that expectations are met, students will have set their expectations for the program accurately and will experience no let down. - Good Design Is Long Lasting
By avoiding the latest trends and fads, a course will never become outdated. Although the developer can refine the information, there will never be any need to start over completely. - Good Design Is Thorough Down to the Last Detail
Nothing about an eLearning design should be arbitrary or left to chance. Instead, every detail should be planned to meet users’ needs and desires. - Good Design Is Environmentally Friendly
The design of any product should contribute to the preservation of the environment by conserving resources as far as possible and minimizing both physical and visual pollution. In terms of an eLearning course, this means improving the learning environment of the students and creating no extra noise or pollution for learners. - Good Design Is as Little Design as Possible
Developers should focus on just the most essential aspects of the course to make it as good as it can possibly be. Adhering to this rule of simplicity ensures that learners only receive as much material as they can absorb.
- Good Design Is Innovative




You can adjust your cookie preferences here.